Uveitis
Uveitis is an inflammatory condition that affects the uvea, the middle layer of your eye. The uvea is a pigmented tissue that nourishes the eye and controls the amount of light entering it. It has three main parts:
- Iris: The colored part of your eye that controls the pupil size.
- Ciliary body: Produces the fluid that nourishes the eye and helps focus your vision.
- Choroid: Supplies blood to the outer layers of the retina.
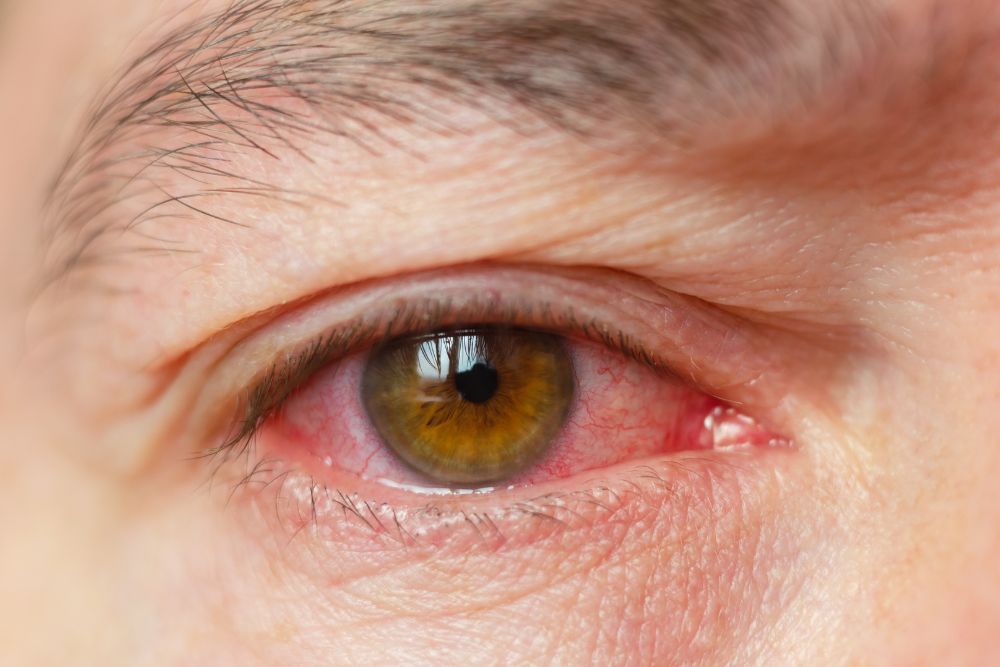
When the uvea becomes inflamed, it can cause a variety of problems, including:
- Pain: Uveitis can cause a dull or aching pain in the eye.
- Redness: The white part of your eye may become red and bloodshot due to inflamed blood vessels.
- Light sensitivity: Your eyes may become more sensitive to light.
- Blurred vision: Inflammation can distort the shape of your eye, affecting how well you see.
- Floaters: You may see small dark spots or floaters in your vision.
There are several different types of uveitis, classified based on the specific part of the uvea that’s inflamed:
- Anterior uveitis: This is the most common type, affecting the iris and the ciliary body.
- Intermediate uveitis: This affects the ciliary body.
- Posterior uveitis: This affects the choroid and the retina.
The cause of uveitis can be unknown (idiopathic) or linked to other underlying conditions such as:
- Autoimmune diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease can sometimes cause uveitis.
- Infections: Viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites can all potentially cause uveitis.
- Injuries: A trauma to the eye can also trigger uveitis.
Uveitis is a serious condition that can lead to permanent vision loss if left untreated. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications. If you experience any symptoms of uveitis, it’s crucial to see an eye doctor right away.